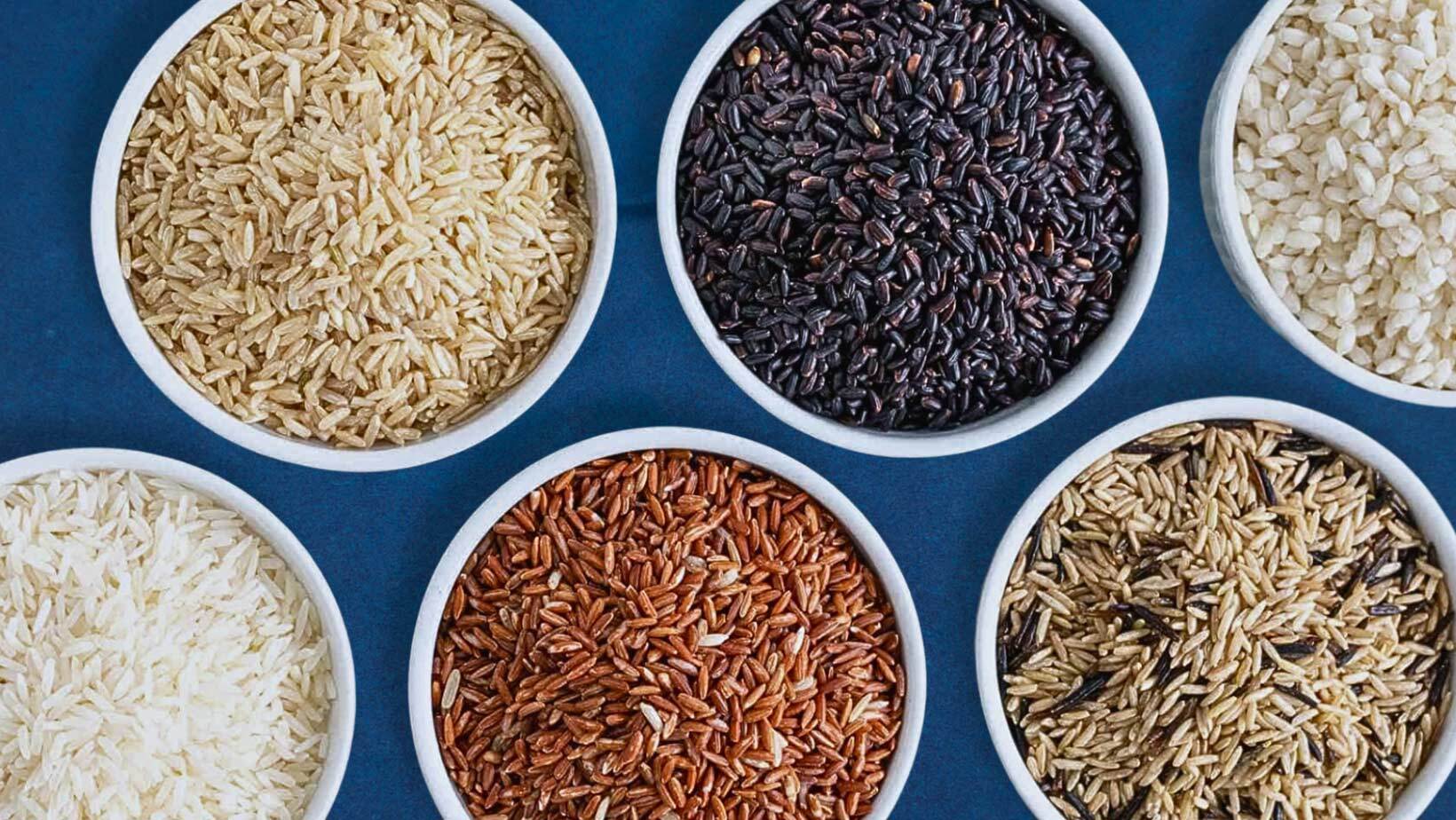

Rice is one of the world’s most essential staple foods. Exploring rice information and gaining knowledge about rice is very important.
Welcome to the rice knowledge blog! Here you will find a wealth of information about rice varieties, Indian basmati rice and non-basmati rice cultivation, and factors considered while choosing rice varieties.
Cultivation of Basmati Rice
Basmati cultivation in India is an important agricultural practice. It is mainly grown in the north Indian states of Haryana, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and parts of Jammu Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. Basmati rice requires specific geographical and climatic conditions, such as fertile soil, a warm climate, and an adequate water supply for cultivation.
Farmers use traditional procedures and present-day techniques to cultivate basmati rice. Farmers follow a careful water supply system to maintain the correct water level in the fields during various stages of rice crop growth.
Additionally, different varieties of basmati rice are cultivated, and each variety has its unique characteristics in terms of aroma, texture, grain size, and flavor. Once basmati rice crops get harvested, rice is dried, processed, and packed for domestic consumption and exported to other countries.
Cultivation of Non-Basmati Rice
The cultivation of non-basmati rice in India is widespread and forms a significant portion of the country’s rice production. Non-basmati rice varieties vary in terms of taste, texture, and aroma compared to premium basmati rice. Farmers across various states, such as West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha, among others, cultivate non-basmati rice due to its higher yield and suitability for different agro-climatic conditions. It plays a crucial role in ensuring food security and meeting the domestic demand for different rice varieties in India.

Here are some essential climate requirements for rice varieties cultivation in India:
Temperature:. The ideal climatic temperature for rice ranges from 25°C to 35°C during the crop-growing season.
Rainfall: Ample water availability is important for rice crop cultivation. It requires yearly rainfall of around 1000-2500 mm, with well-distributed rain showers during the monsoon months (June to September)
Soil Type: Rice can be cultivated in different varieties of soils, but it mainly prefers well-drained, fertile lands with good water retention value. Clayey or loamy soils suits for rice cultivation.
Rice-Grown Seasons: Main rice-growing season months in India are the Kharif season (June to September) and the Rabi season months (November to April). The choice of rice varieties and their cultivation practices can vary based on these seasons.
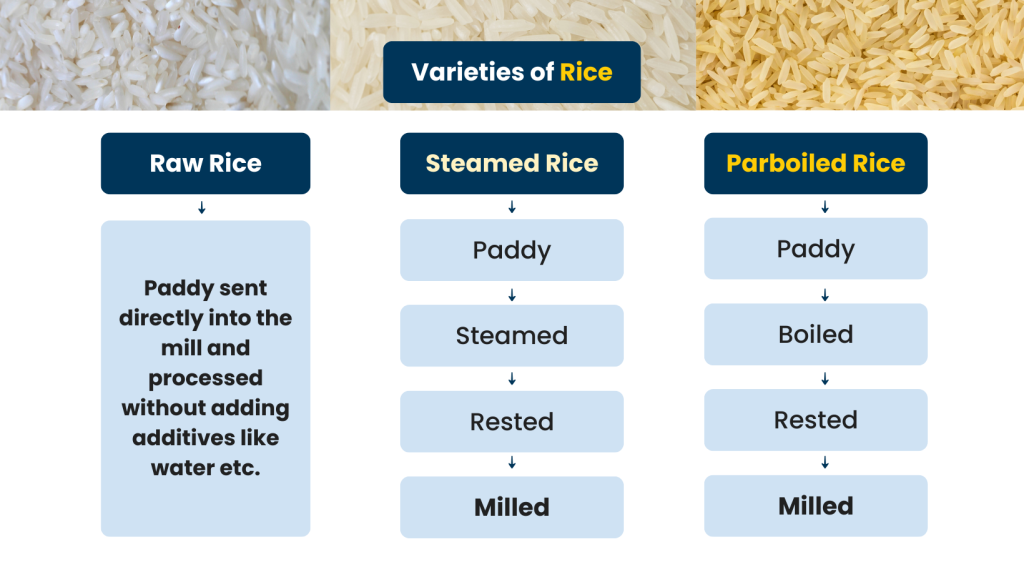
Let’s explore the varieties of rice in India and their processing procedure
| SNo | Rice Type | State | Rice Varieties |
| 1 | Basmati Raw | Haryana | Pusa Raw, PR 47 Raw, Sugandha Raw, 1718 Raw, 1121 Basmati Raw, PR – 11 / 14 Raw, Sharbati Raw, |
| 2 | Basmati Raw | Punjab | 1121 Basmati Raw, Pusa Raw |
| 3 | Basmati Steam | Haryana | 1509 Basmati Steam, Pusa 1401 Steam, 1121 Basmati Steam, Sugandha Steam, PR 47 Steam, 1718 Basmati Steam, PR 11/14 Steam, 1401 Basmati Steam, Sharbati Steam. |
| 4 | Basmati Steam | Punjab | PR – 11/14 Steam New, 1718 Basmati Steam, Sharbati Steam, 1121 Basmati Steam, Mogra 1121, Sugandha steam, Dubar 1121, 1401 Basmati Steam, Tibar 1121, 1509 Basmati Steam. |
| 5 | Basmati Steam | Uttar Pradesh | Sharbati Steam |
| 6 | Basmati Sella | Haryana | 1718 Golden Sella, 1121 Basmati Golden Sella, Sharbati Sella, 1401 Basmati Golden, 1718 White Sella, 1121 Basmati White Sella, Pusa 1401 Golden Sella, 1401 Basmati White Sella, PR – 11/14 Golden Sella, Pusa 1401 White Sella, PR 47 Golden Sella, 1509 Basmati Golden Sella, PR – 11 / 14 Sella, Sugandha Golden Sella, PR 47 Sella, 1509 Basmati White Sella, Sharbati Golden Sella, Sugandha Sella |
| 7 | Basmati Sella | Punjab | 1401 Basmati Golden Sella, 1121 Basmati Golden Sella, Pusa White Sella, 1509 Basmati Golden Sella, 1121 Basmati White Sella, Sharbati White Sella, 1509 Basmati White Sella, RH 10 White Sella, Sughandha Sella, 1718 Basmati Golden Sella, PR – 11/14 Sella, 1401 Basmati White Sella, 1718 Basmati White Sella, PR – 11/14 Golden Sella. |
| S No | Rice Type | State | Rice Varieties |
| 1 | Non Basmati Rice | Andhra Pradesh | Pure BPT Raw New, NLR BPT Raw New, Swarna Raw 5% Broken Fresh Milling, IR 64 Raw 5% Broken Fresh Milling, Swarna Raw 5% Broken Rice to Rice, 100% Raw Broken, |
| 2 | Non Basmati Rice | Bihar | Sona Raw, Katarni Raw, Parmal Raw. |
| 3 | Non Basmati Rice | Chhattisgarh | IR- 64 Raw 5% Broken Rice to Rice, RB Gold 5% Raw, Swarna Raw New, 5%Broken Fresh Milling |
| 4 | Non Basmati Rice | Gujarat | IR 64 Raw 5% Broken, Shree RamWada, Kolam Raw Rice, IR 64 Raw 5% Broken Fresh Milling, 100% Raw Broken. |
| 5 | Non-Basmati Rice | Karnataka | Sona Masuri Raw, RNR Raw New, Sona Masuri Raw. |
| 6 | Non-Basmati Rice | Kerala | Kaima Rice |
| 7 | Non-Basmati Rice | Kolkata | Swarna Raw 100% Broken, Swarna Raw 5% Broken Fresh Milling, Gobind Bhog Raw New, Gobind Bhog Raw Old, 100% Raw Rejection Rice. |
| 8 | Non-Basmati Rice | Madhya Pradesh | Swarna Raw 5 % Broken |
| 9 | Non-Basmati Rice | Maharashtra | IR 64 – 100% Broken Raw Rice Milling, Samba Masoori Raw, HMT Raw Old, IR 64 – 5% Broken Raw Rice, BPT Raw Old, HMT Raw New, Kolam Raw Old, BPT Raw New, Wada Kolam Raw Rice, Kolam Raw New, JSR Raw Old, Swarna Raw 5% Broken, BPT Raw New, Kolam Raw New. |
| 10 | Non-Basmati Rice | Odisha & North East | Swarna Double Boiled, Swarna Single Boiled, IR 64 Parboiled 5% Broken, IR 64 Raw 5% Broken. |
| 11 | Non-Basmati Rice | Tamil Nadu | Seerga Samba |
| 12 | Non-Basmati Rice | Telangana | BPT Raw New, JSR Raw Old, Kolam Raw New, Samba Masoori Raw, HMT Raw Old, BPT Raw Old . |
| 13 | Non-Basmati Rice | Uttar Pradesh | Swarna Raw 5% Broken HMT Raw |
| S No | Rice Type | State | Rice Varieties |
| 1 | Non-Basmati Steam | Andhra Pradesh | Non BPT Steam NLR Sona Steam New HMT Steam GR-11 Steam Pure BPT Steam |
| 2 | Non- Basmati Steam | Bihar | Sona Steam |
| 3 | Non- Basmati Steam | Karnataka | Sona Masuri Raw RNR Raw New Sona Masuri Raw |
| 4 | Non- Basmati Steam | Maharashtra | BPT Steam Kolam Steam Rupali Steam |
| 5 | Non- Basmati Steam | Tamil Nadu | Rajabhogam Ponni Steam |
| 6 | Non- Basmati Steam | Telangana | BPT Steam New Kolam Steam New HMT Steam JSR Steam RNR Steam |
| 7 | Non- Basmati Steam | Uttar Pradesh | Sona Masuri Steam |
| S.No | Rice Type | State | Rice Varieties |
| 1 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Andhra Pradesh | Idly Rice ADT-37 Parboiled, Swarna Half Boiled, Jaya Parboiled, Non BPT Parboiled, IR-64 Parboiled, HMT Parboiled, GR-11 Parboiled, Kuruva Parboiled, Idly Parboiled, Rejected Rice Parboiled, Jaya Parboiled. |
| 2 | Non- Basmati Parboiled | Bihar | Mansoori Parboiled, Katarni Parboiled. |
| 3 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Gujarat | Ir-8 Parboiled 5% Broken IR-64 Parboiled 5% Broken |
| 3 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Chhattisgarh | IR-64 Parboiled 5% Broken Paddy Milling |
| 4 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Karnataka | Rose Matta, RNR Boiled, Sona Ponni Half Boiled, Sona Full Boiled |
| 5 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Kerala | Thanjavur Ponni, Matta Short Grain, Matta Long Grain |
| 6 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Kolkata | Swarna Parboiled 100% Broken Swarna Parboiled 5% Broken 1010 Parboiled Basmati Parboiled IR-64 Parboiled 100% Broken Ratna IR-64 Parboiled 5% Miniket |
| 7 | Non- Basmati Parboiled | Maharashtra | IR-64 Parboiled 100% Broken IR-64 Parboiled 5% Broken BPT Boiled |
| 8 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Tamil Nadu | 12Month Old Raj bhog Karnataka Ponni Boiled ADT 45 Parboiled New Thanjavur Ponni Boiled, HMT Boiled 1 Year Old HMT Boiled BPT Ponni |
| 9 | Non-Basmati Parboiled | Odisha | IR-64 Parboiled 5% Broken Swarna Double Boiled 5% Broken Swarna Single Boiled 5% Broken |
Points to be checked while buying rice

Chalkiness Percentage
The opaque portion found in the rice grain is the chalky portion. Rice chalkiness measurement methods are mainly based on naked-eye observation or area-based 2D image analysis and using the milled rice kernel as the material
Whiteness
The whiteness meter gives accurate rice whiteness values. Just place the whiteness meter on the rice and read the value. Brown rice shows 20 and well-milled rice shows 40.
Discolor and Damage of Rice
The grains may be infected by various organisms before or after harvesting causing discoloration, also harvest season and locality will change the color of grains. Rice damage caused due to insects.
Broken Rice
Paddy rice produces around 50% whole rice, 16% broken rice, 20 % husk, and 14% bran and meal.
Moisture Content of Rice
Moisture content before milled will be 12 to 14 % and further reduced to 9% after the milling procedure.
Rice Grain Sizes
Rice grain sizes are classified as short-grain, medium-grain, and long-grain based on their length and width ratio when cooked.

| S No | Basmati Rice Type | Rice Size (As per 2022 Crop) |
| 1 | 1121 Basmati Rice | 8.35 mm |
| 2 | 1718 Basmati Rice | 8.35 mm |
| 3 | 1509 Basmati Rice | 8.40 mm |
| 4 | 1401 Basmati Rice | 7.70 mm |
| 5 | Pusa Basmati Rice | 7.45 mm |
| 6 | Traditional Basmati Rice | 7.25 mm |
| 7 | Sugandha Basmati Rice | 7.90 mm |
| 8 | Sharbati Non-Basmati Rice | 7.10 mm |
| 9 | PR 11/14 Non-Basmati Rice | 6.90 mm |
| 10 | Parmal Non-Basmati Rice | 6.40 mm |
Non-Basmati Rice < 6mm
RNR – 5.2 mm
Sona Masuri -5.2 mm to 5.5 mm
Swarna -5.5 mm
IR64 – 5.8mm to 6mm
Rice is a symbol of cultural identity and an economic source for many nations. Understanding its significance is very important and developing a prosperous future for both rice-dependent countries and the global food system is essential.
